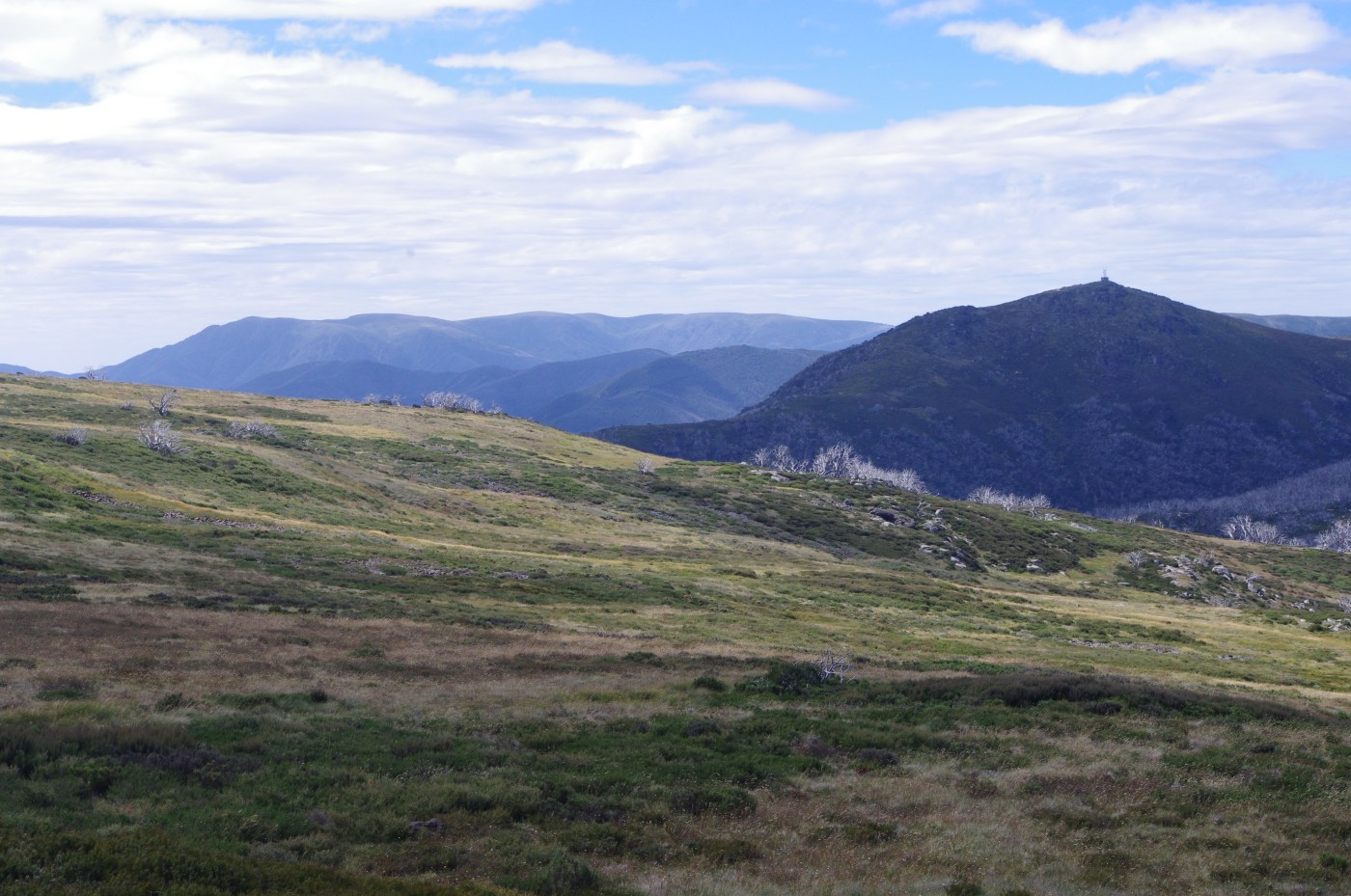
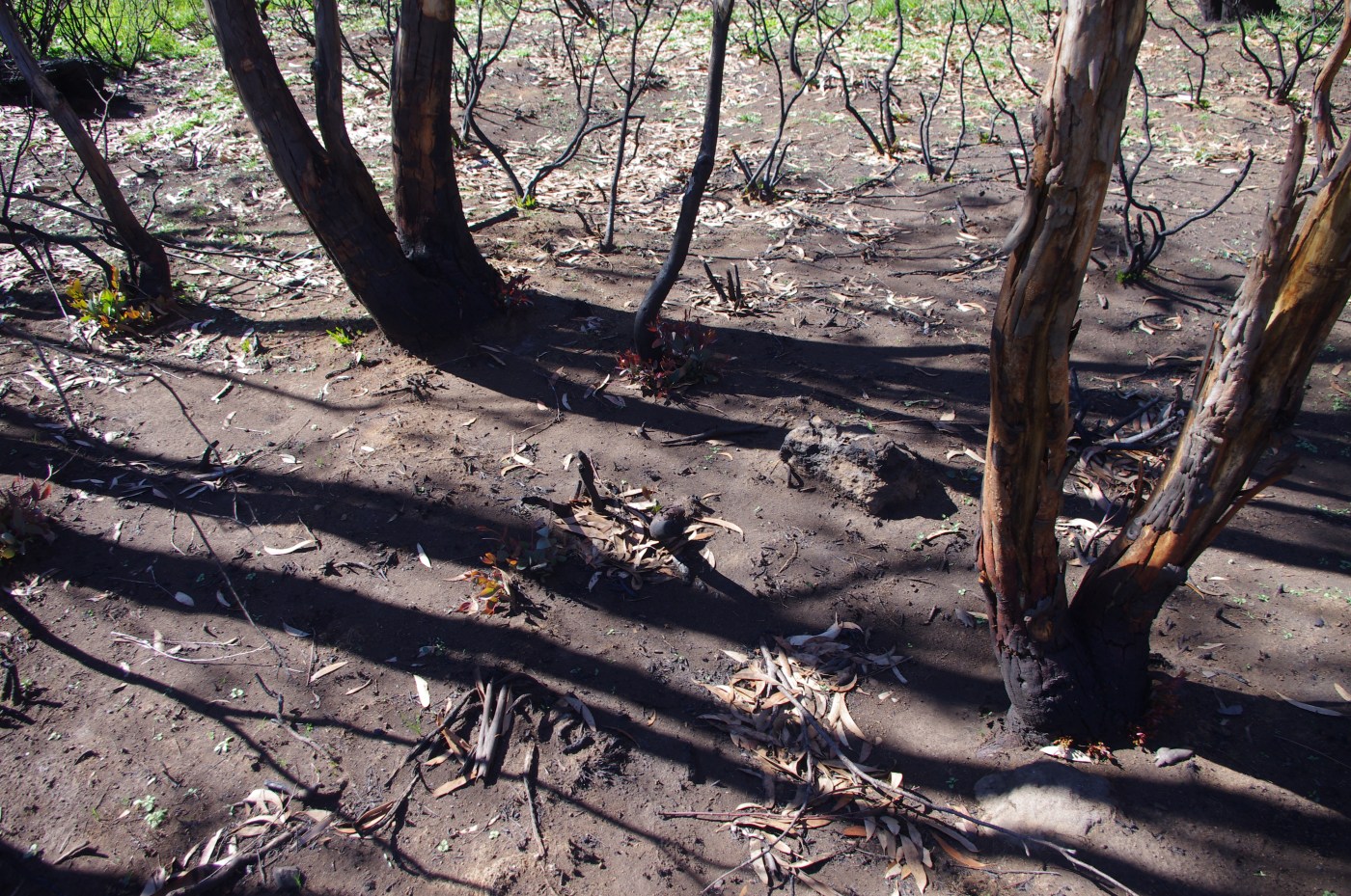
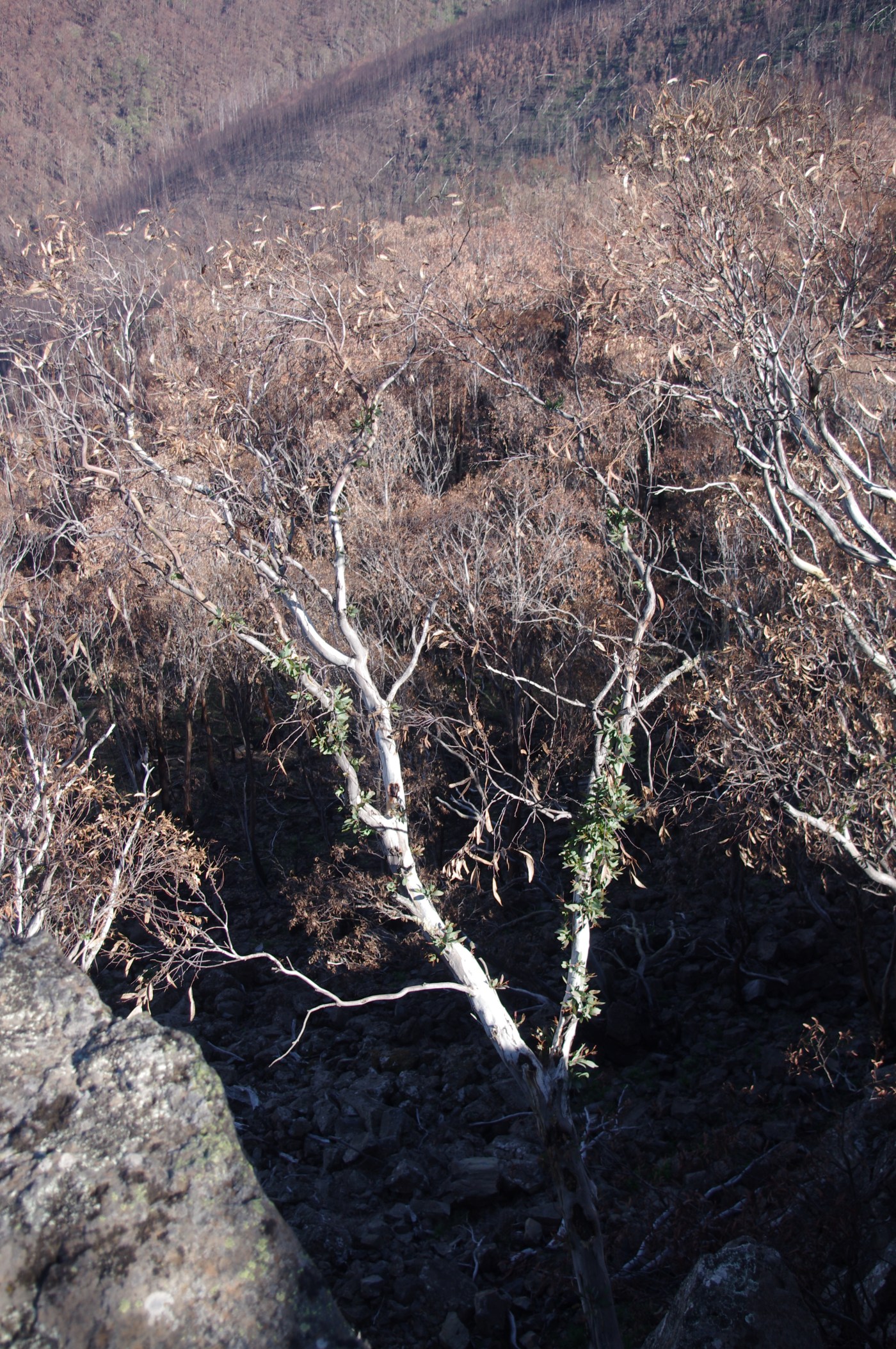
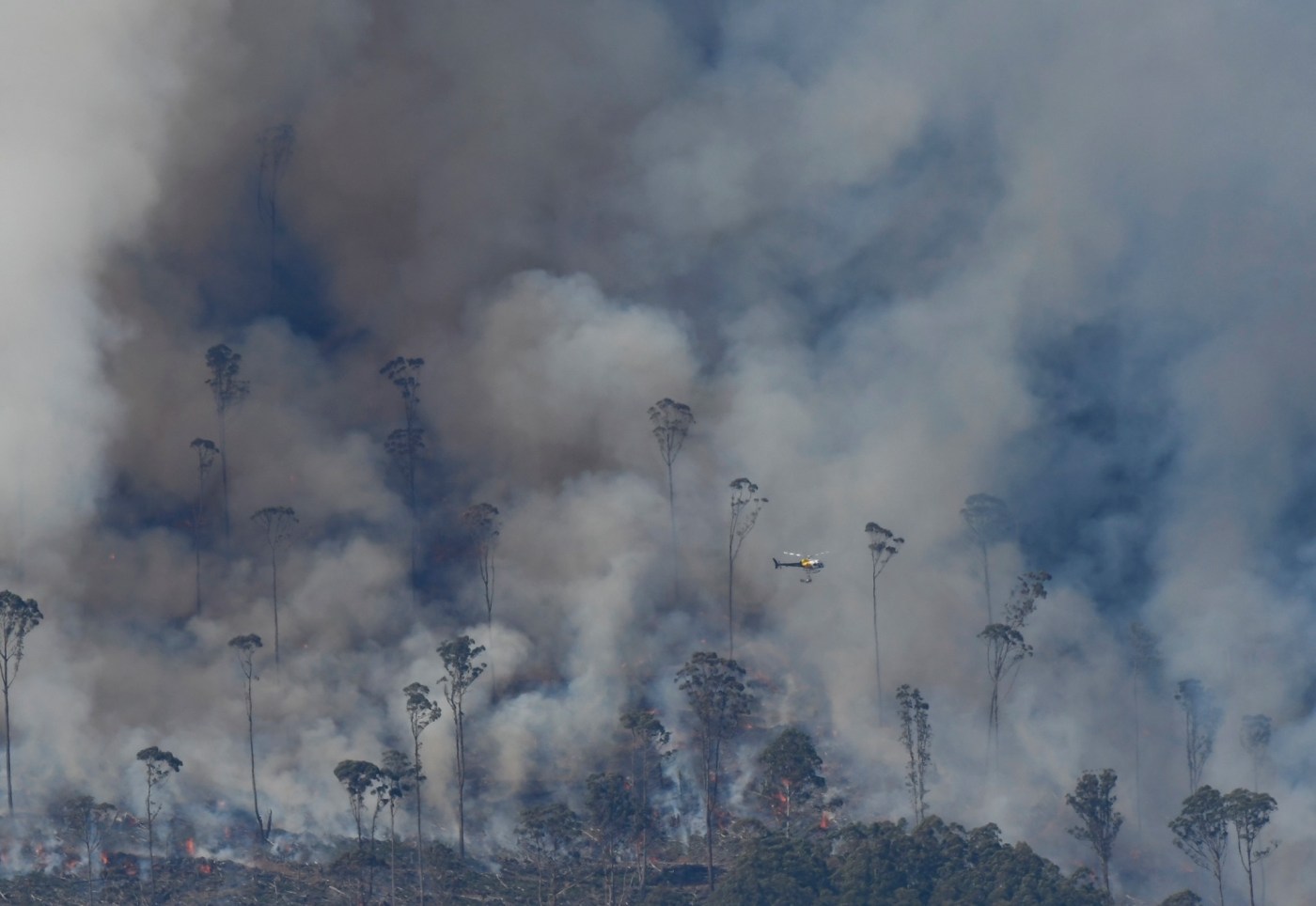
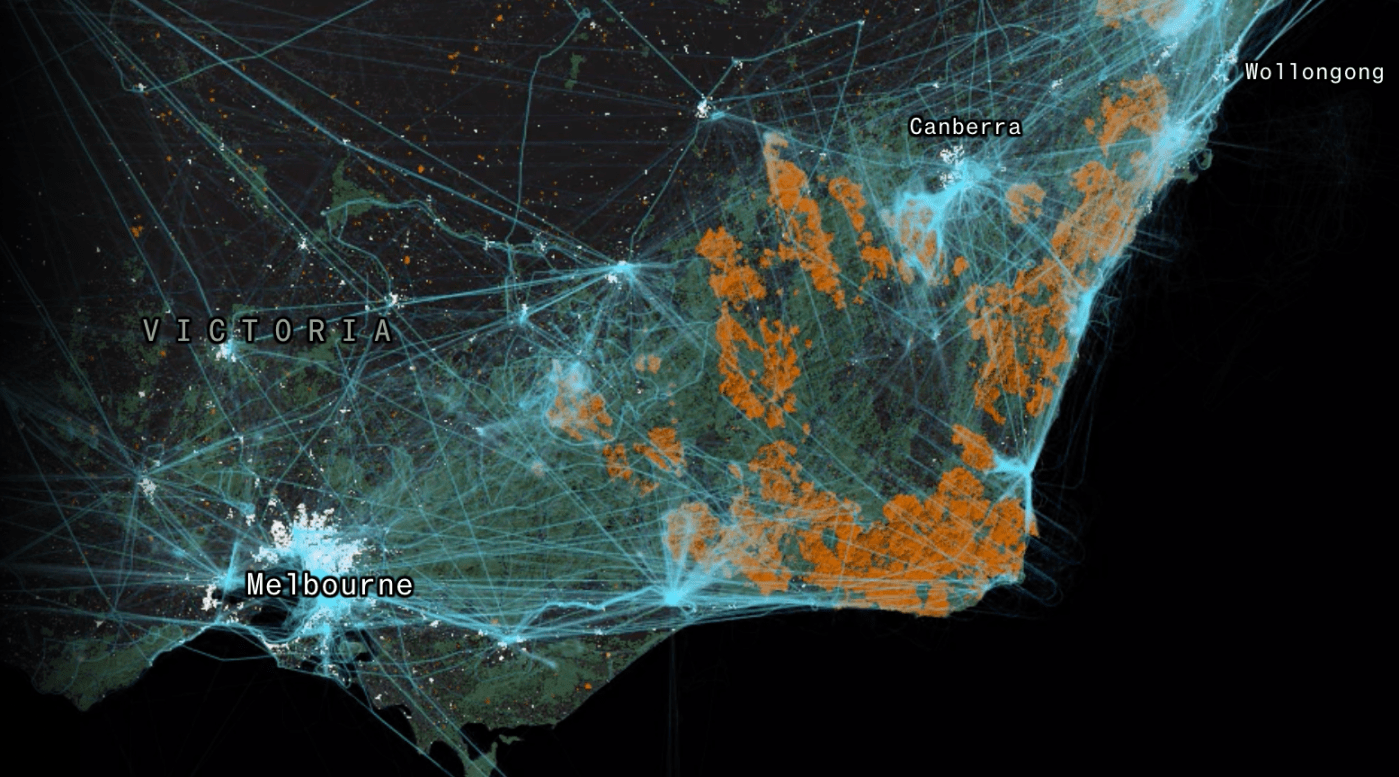
Australia just had its hottest, driest year on record, with fires starting in the winter months and burning in some places until early March. Much of the Alps, including the Snowy Mountains, Upper Murray, Eastern Alps and East Gippsland were burnt. Then, as we started to get on top of the worst of the fires, the mountains of the ACT went off, with enormous blazes that devastated the high country of Namadgi National Park.
Thousands of volunteer and career firefighters battled these blazes. As is normal practise, states helped each other out by sending teams and resources. My CFA brigade sent strike teams to NSW and then Mallacoota. By February we were asked to send teams to the ACT fires. We were fighting fires at home too, and we were all bloody glad when the rains came in mid February.
As fire seasons get longer because of climate change, the prospect of fighting local fires and also having to support other states for larger sections of the year is daunting for fire fighters. Helping each other out is second nature to firefighters, and a tradition we will maintain. But longer fire seasons does mean greater impact and time away from home and work for volunteers. It means greater expenditure on career firefighters. It means greater wear and tear on trucks and other equipment if they are being used for more of the year. It is also a problem for those who have to ensure we have adequate air support to be able to fight fires. Because many of the firefighting aircraft are leased, and shared around the world, as fire seasons get longer, there will be ever more demand, and greater cost, to secure the fleet we need.
A recent report in Bloomberg by By Mira Rojanasakul and Hayley Warren highlights the scale of the firefighting effort that happens, and the cost of keeping planes and helicopters on the fireground.
Continue reading “Shared Firefighting in a hotter world” →


































































Recent Comments