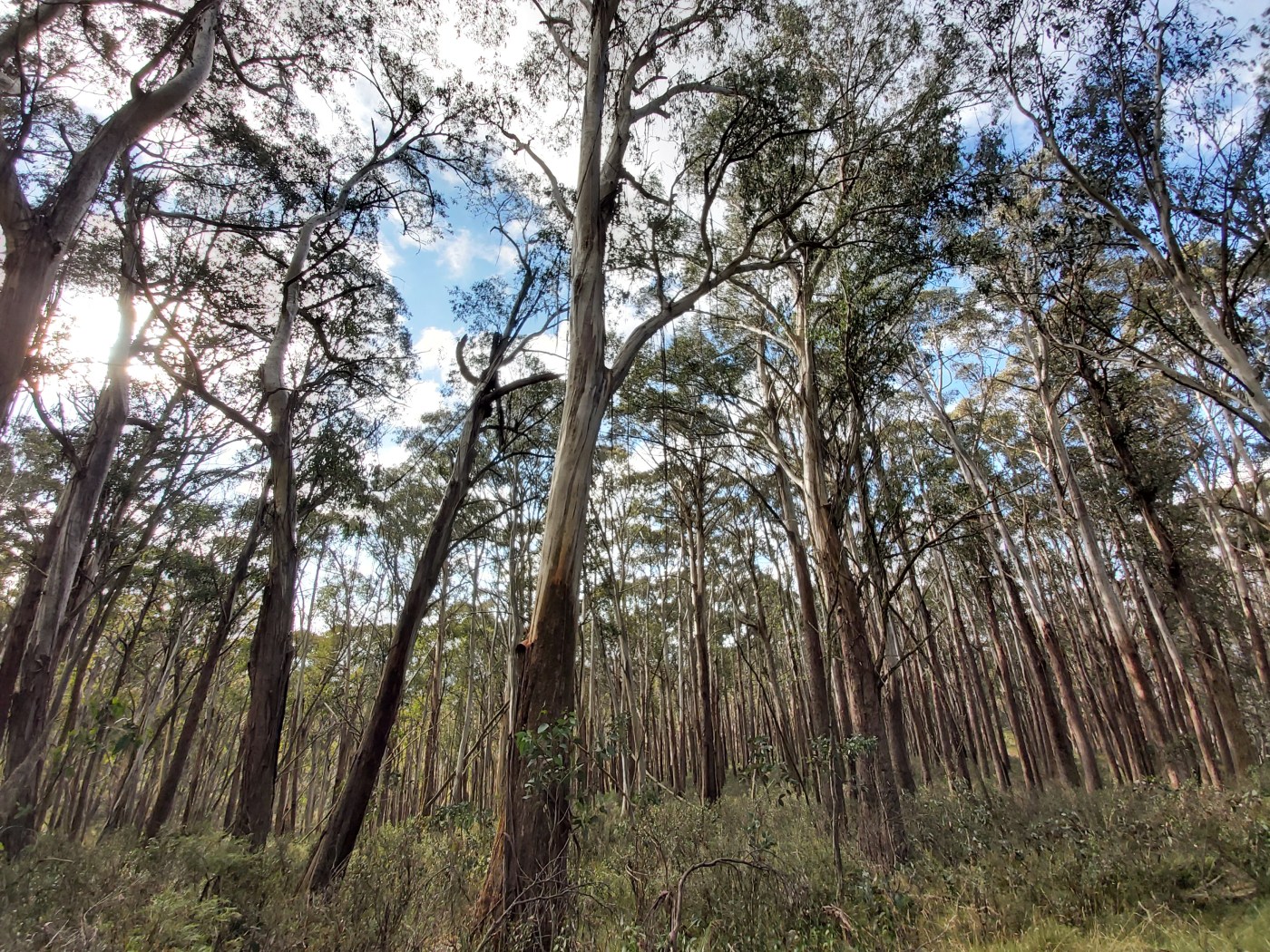
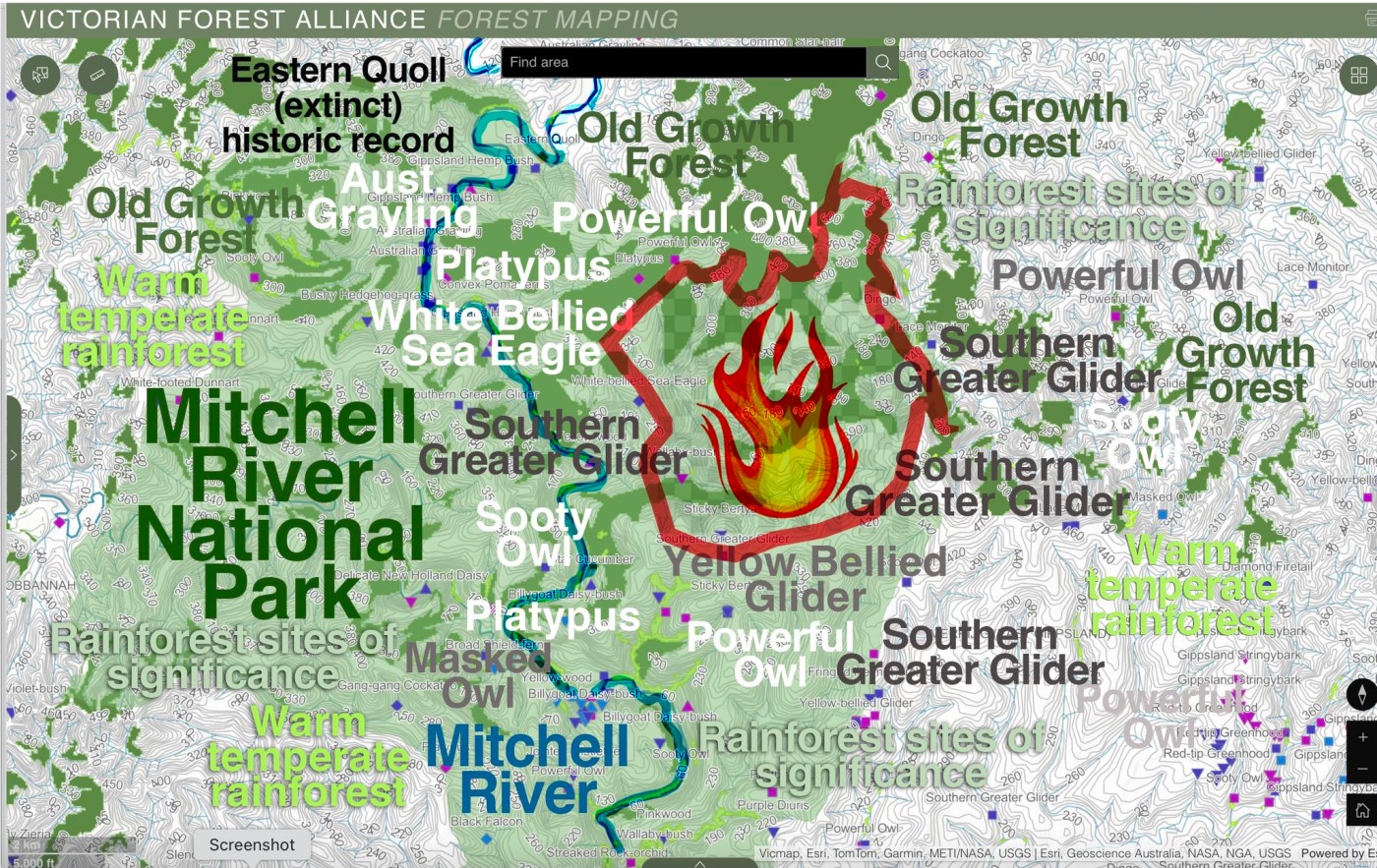
Ash forests – forest comprised of Mountain Ash, Alpine Ash, or sometimes both – are some of the most iconic forest types in Victoria, or even the world. Covering around 500,000 ha of Victoria and stretching from the Otways to the north-eastern boundary with NSW, their stronghold is in the Central Highlands to the east of Melbourne and through the higher ranges of Gippsland and the north east of the state.
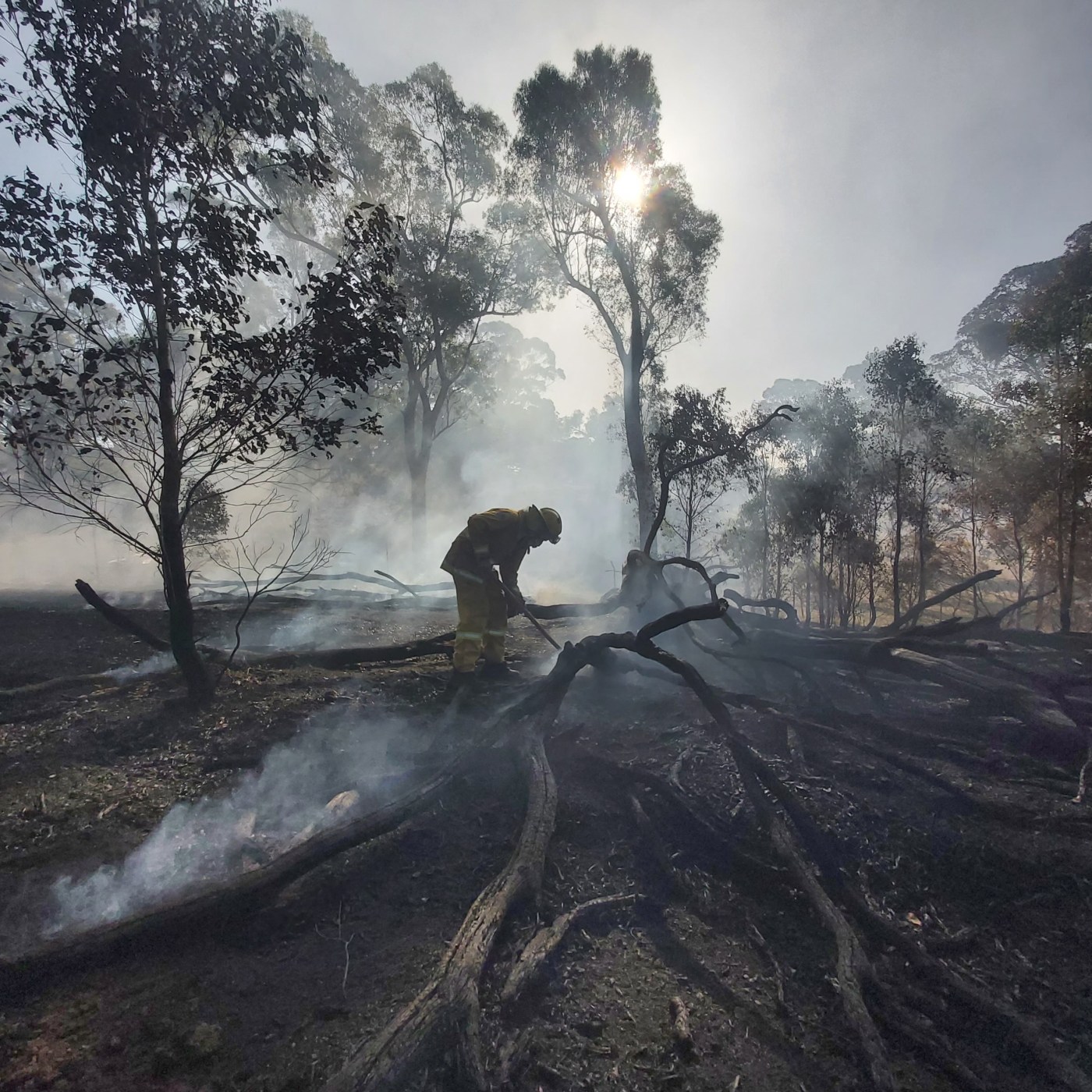
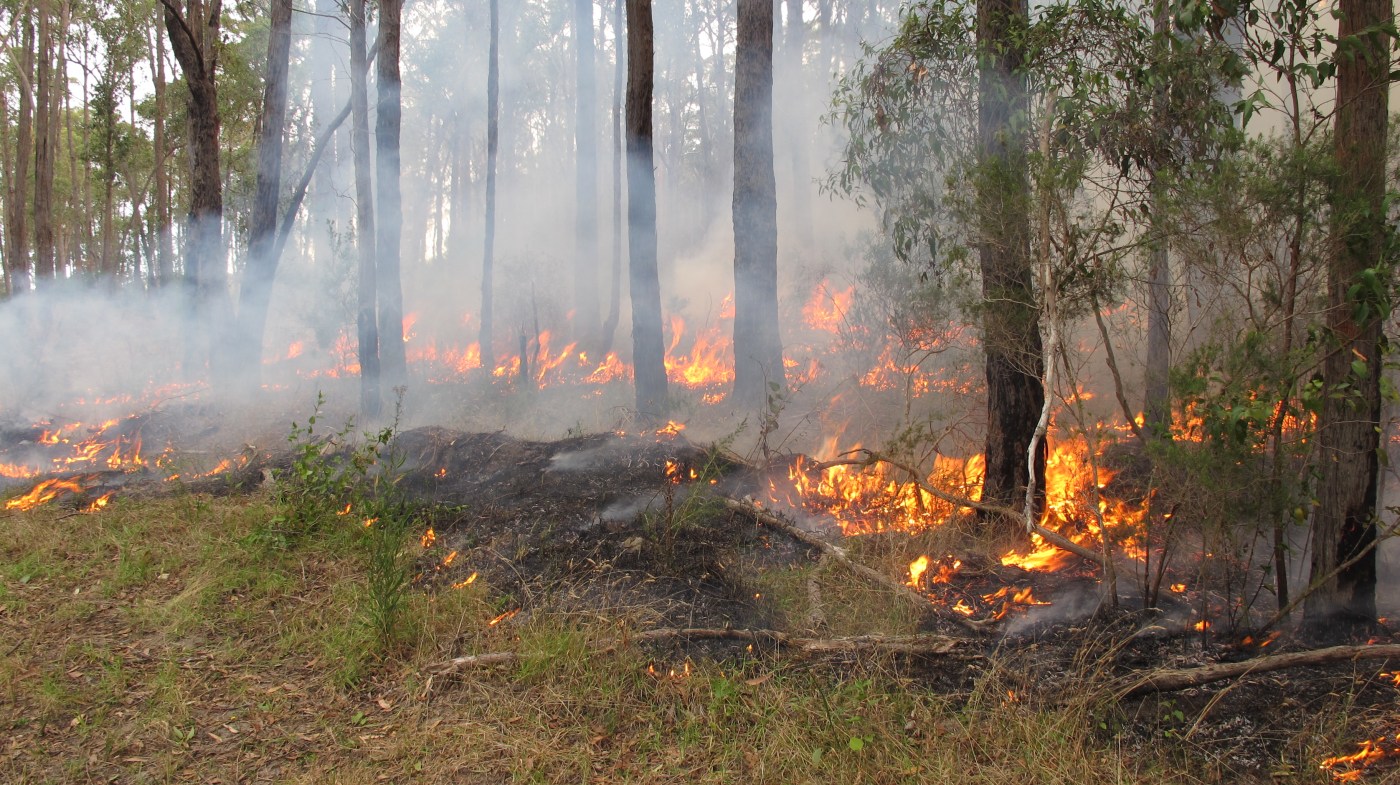
These forests have a complex relationship with fire: these forests can live with some fire – but not too much. Scientifically known as ‘obligate seeders’, after severe bushfire, ash forests are killed, but prolifically regenerates from canopy stored seed. The important point here is that these slowly regenerating forests cannot produce seed for 20 years after they regenerate from fire. This means they are highly vulnerable to shortened fire intervals – the exact challenge that land managers in Victoria are facing with climate change.
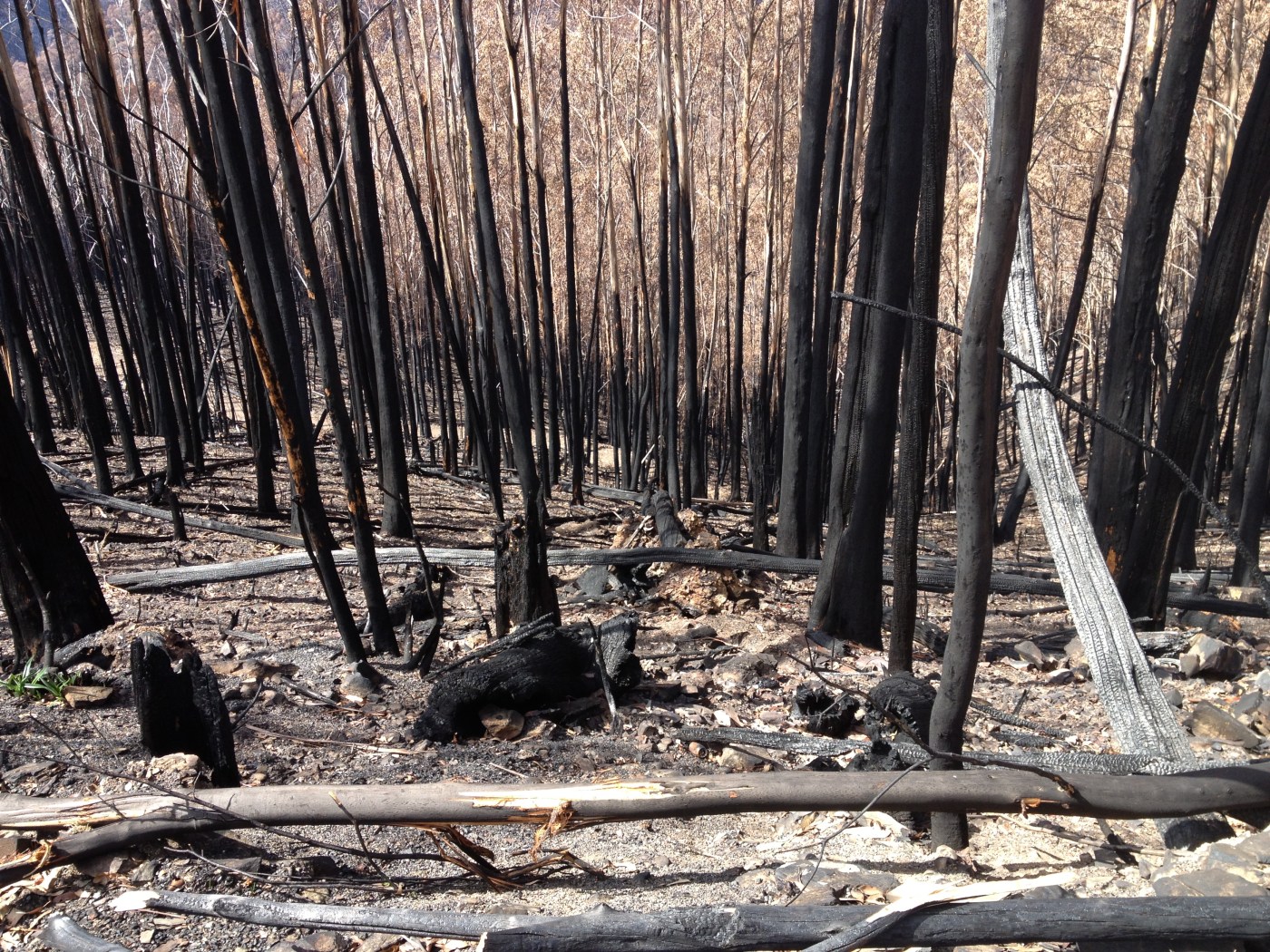
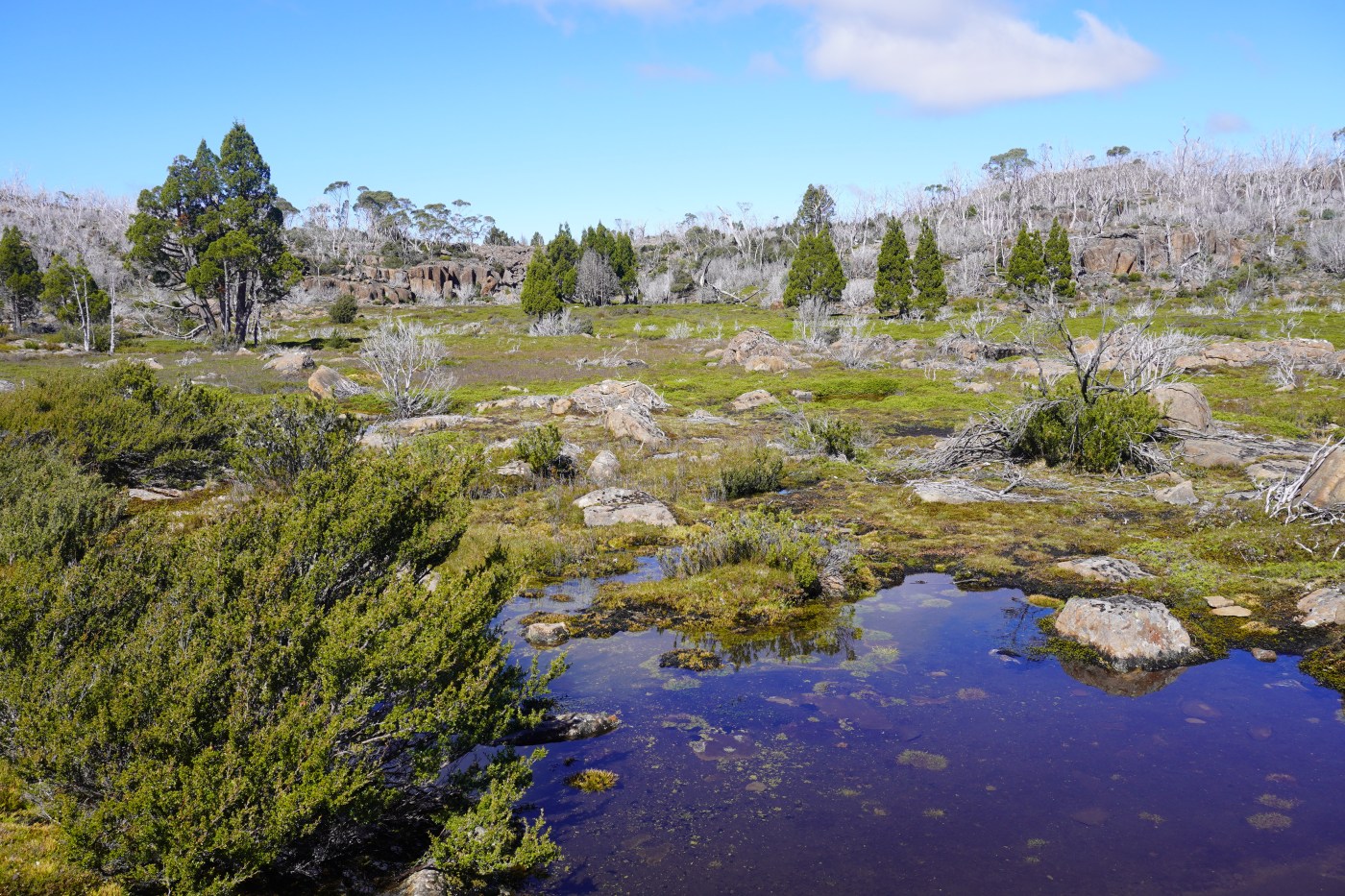
Once a mountain ash or alpine ash forest has burnt numerous times, it may eventually fail to regenerate, which can lead to population collapse and a change of ecosystem type. This sounds simple, but ecologically, this is dramatic. A tall forest – high in carbon stocks and habitat – changes rapidly to a short shrubland or grassland.
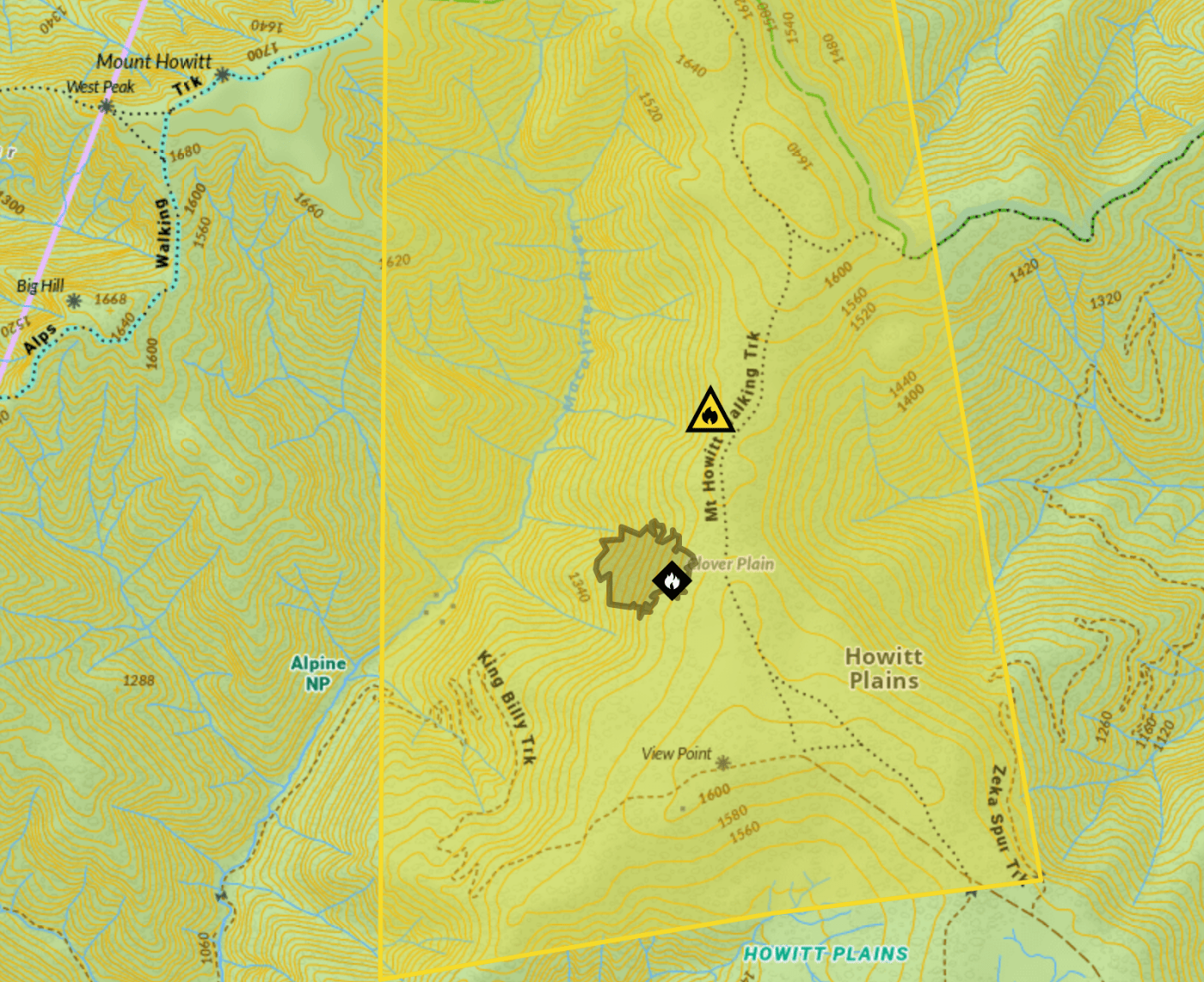
This not theory. This situation already exists among alpine ash forests. The massive bushfires in 1998, 2003, 2006, 2009, 2013, 2014 and 2019/20 and meant that over 97% of Alpine Ash distribution burnt. These fires overlapped and some areas burnt two to three times across two decades (Fagg et al. 2013; Bassett et al. 2021), leaving 43,000 ha of Alpine Ash forest at risk of collapse (Fairman, 2023).
Mountain Journal has long reported about threats to Ash forests and the need for greater government intervention (check here for some of the articles).
Now people involved in the recovery of Ash forests have recently spoken out about the threats posed to these forests.
Continue reading “VIC government must increase efforts to sustain Ash forests”

































































Recent Comments