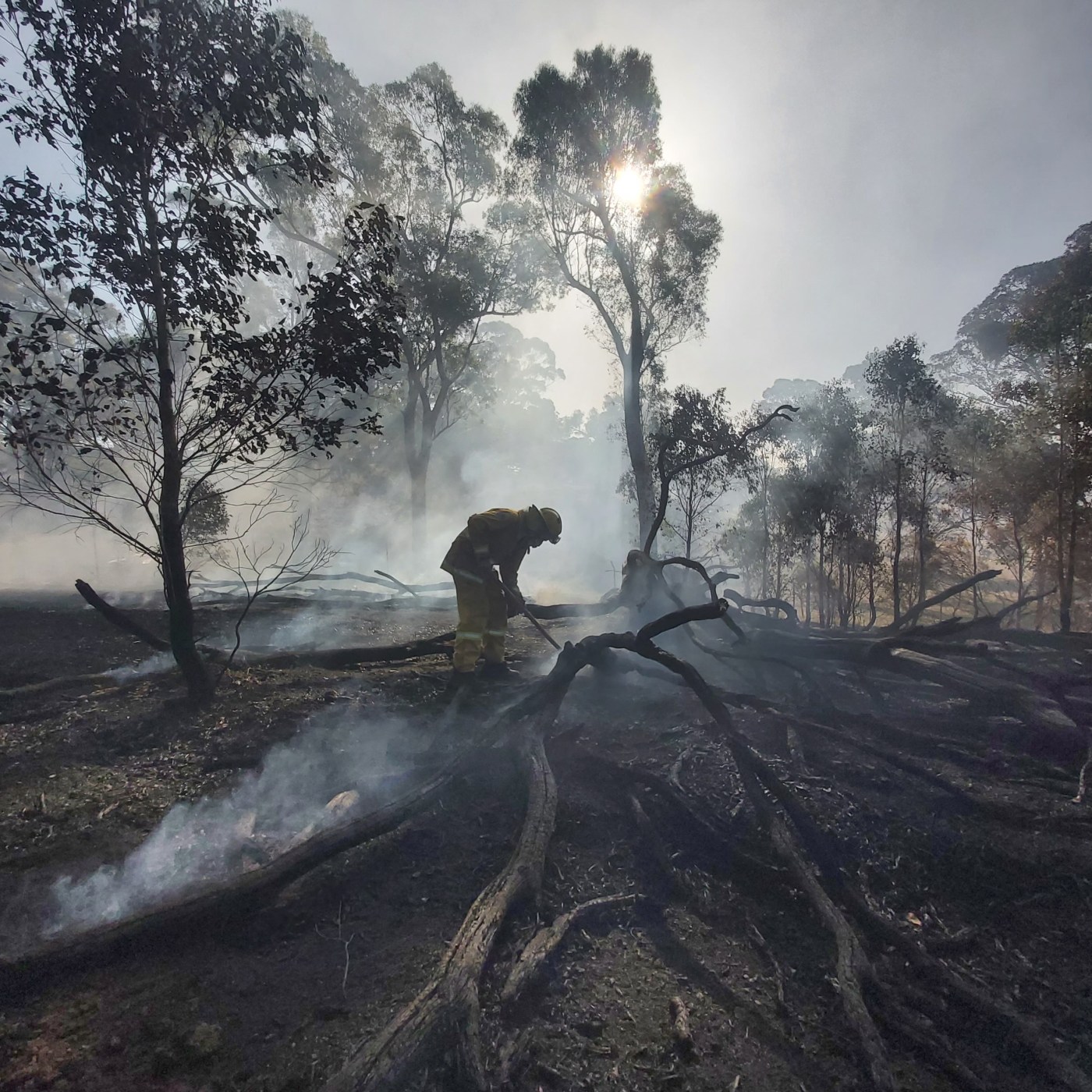
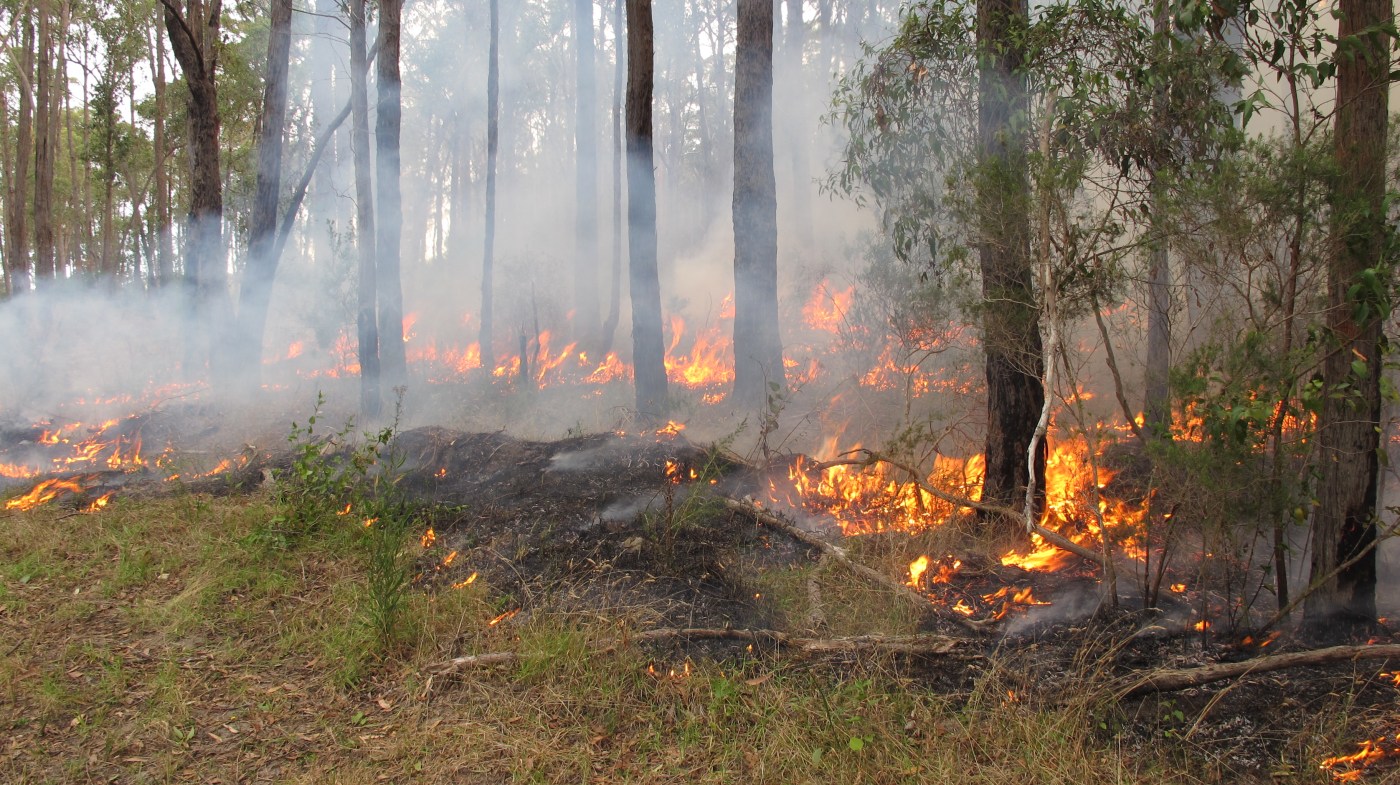
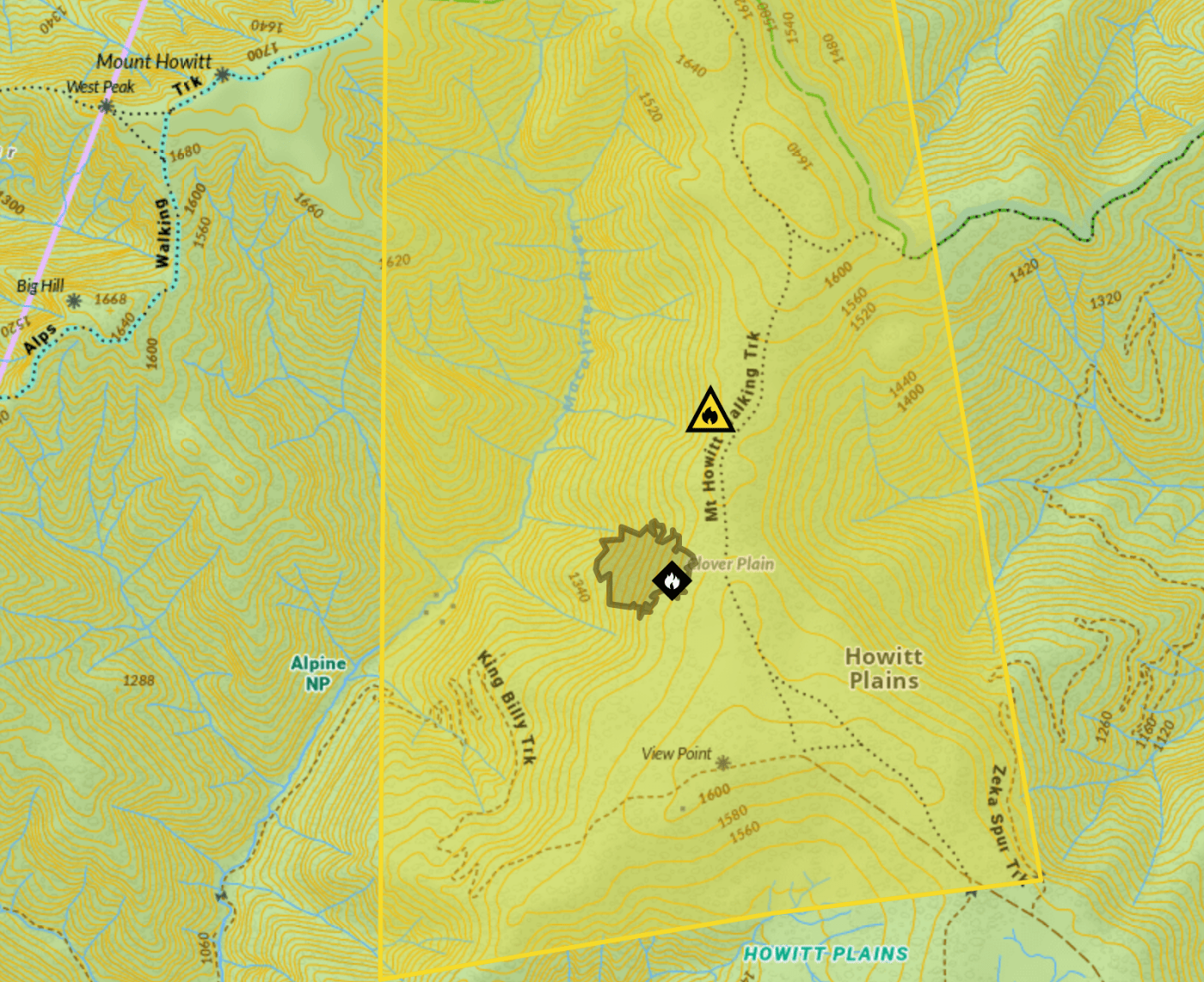
Recent dry lightning caused a number of fires across the Victorian high country. Most were quickly contained but one just north of the Howitt Plains is becoming a concern.
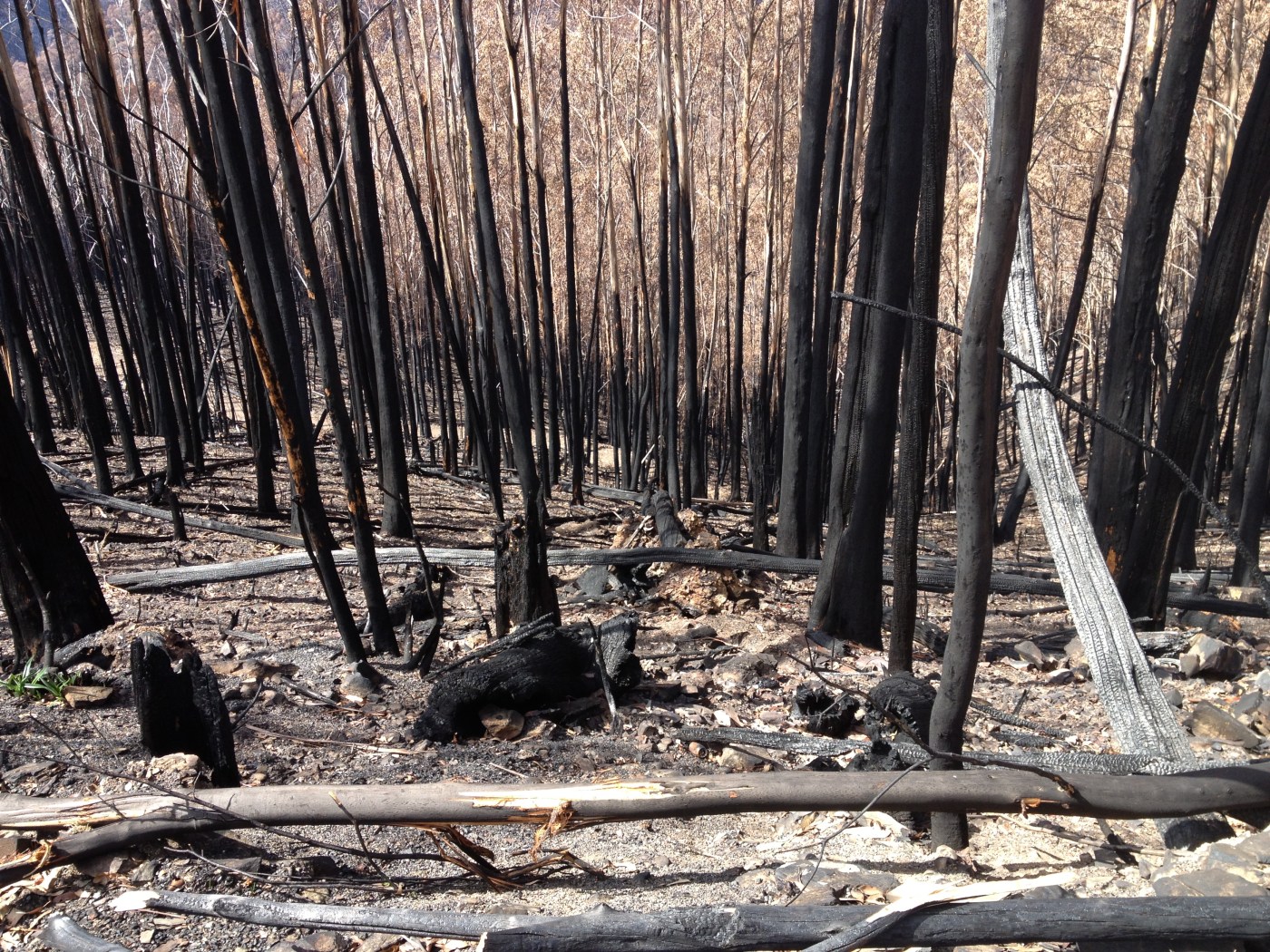
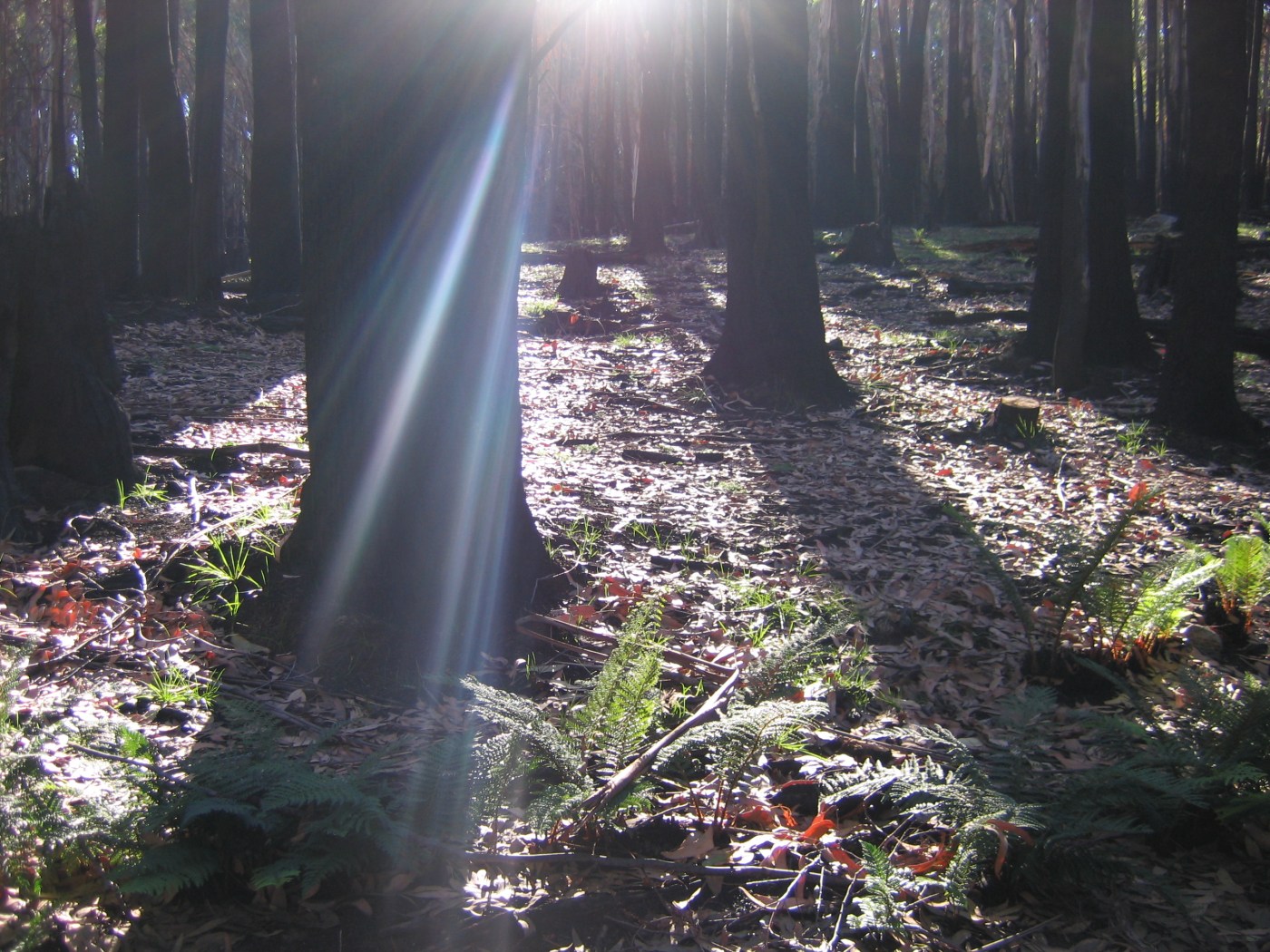
This area, of high elevation snow gum woodlands inter-spaced with grass dominated plains, has been burnt several times in recent decades, with many areas now holding thick (and highly flammable) regrowth forests. Fires in these recovering forests can lead to ecological collapse – that is, the loss of snow gum dominated forests, which are replaced by grass and shrubs. It is essential that we exclude fire from these ecosystems as they recover.


































































Recent Comments