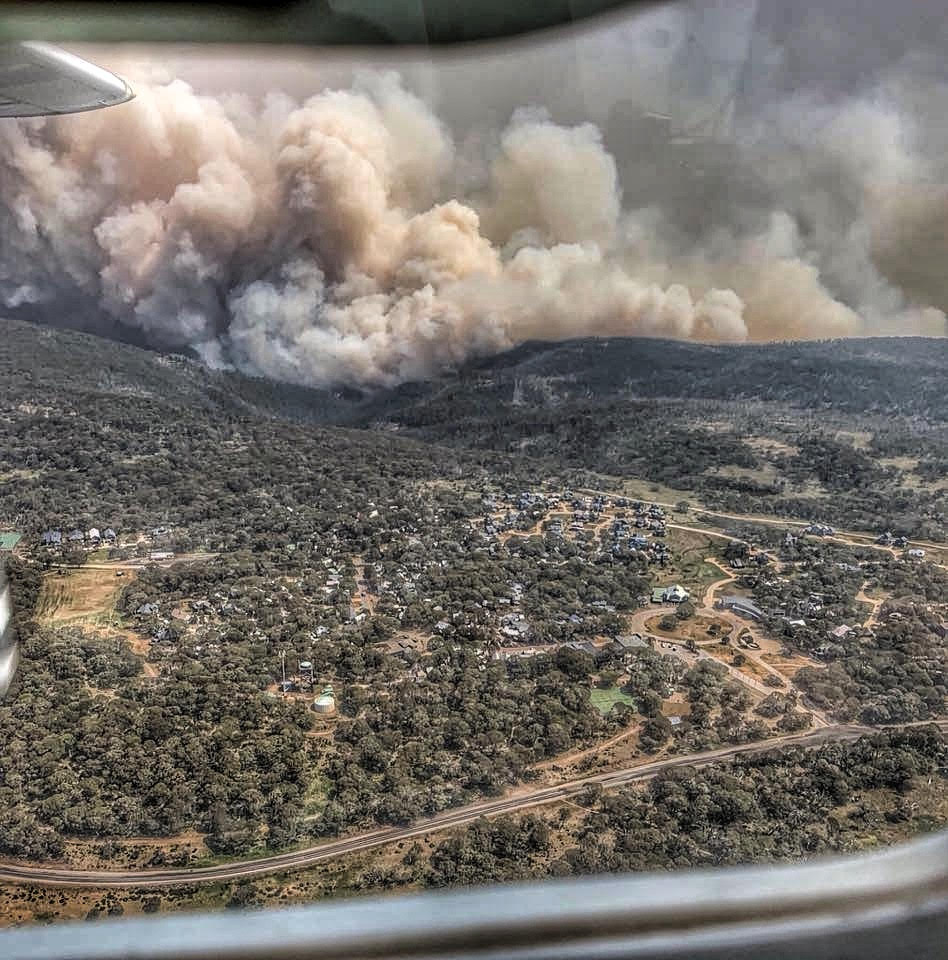
The Tasmanian National Parks Association (TNPA) recently dedicated an issue of their newsletter to the question of how to manage wild fire in Western Tasmania. As has been widely noted, including here at Mountain Journal, fires having been getting more intense in western lutruwita/ Tasmania since a ‘tipping point’ sometime around the year 2000. Since then, there has been an increase in the number of lightning-caused fires and an increase in the average size of the fires, “resulting in a marked increase in the area burnt”.
As TNPA notes in the introduction:
The direct impacts of climate change for Tasmania are changes to weather patterns with corresponding changes to levels of temperature, rainfall and evaporation – most likely a warmer, drier climate overall.
The outcomes of some of these changes are beyond our ability to influence. For example, there are no options for protecting an entire landscape from drought, although it may be possible to save examples of individual species.
As discussed in the following essays, the increased frequency and intensity of wildfires is already resulting in demonstrable impacts on some of Tasmania’s most highly valued species and ecosystems (paleoendemics and alpine ecosystems) and options do exist for how it is managed.
Continue reading “Fire: how do we control things when we can’t control things?” →
































































Recent Comments